|

|
|
|
Broadband
Over Powel Line (BPL) Technology
|
2 Broadband over Power Line (BPL)
2.1 BPL Technology.
2.2 BPL Solutons.
2.4 Internet Service Comparison.
2.6 Global BPL usage.
4 Glossary.
This document provides information and background on the subject of Broadband over Power Line (“BPL”) and discusses how BPL is a core communications technology that can be applied to a utility's electrical grid (“Grid”) to facilitate the creation of a SMART GRID. The SMART GRID enables Distribution Automation for the Electricity Utility Company (“Utility”). The SMART GRID encompasses extensive utility applications as well as enables Broadband applications to be delivered to consumers.
A detailed description of the various broadband applications that would be enabled by BPL is beyond the scope of this paper.
This document has been developed by ElectroNet as part of their proposed project to develop a BPL service over the Utility Grid.
BPL is a recently commercialized technology that allows broadband Internet (using Internet Protocol - IP) to be transported over the Grid at speeds ranging from 4Mbps to 145Mbps for delivery of IP data traffic and applications to homes and businesses on a shared basis.
The diagram below (BPL Architecture) shows IP data from the Internet being injected at the HV/MV substation, travelling through the electrical grid and being accessed by consumers using a BPL modem at their premises.
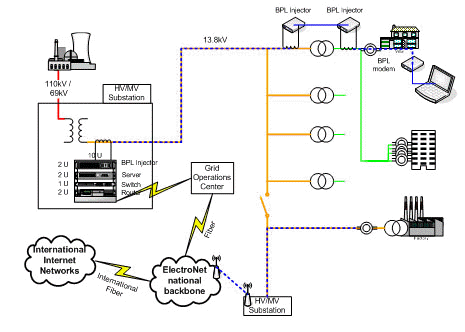
BPL Architecture
The BPL equipment injects the IP data as an RF signal into the overhead or underground power lines using ferrite cores. The RF signal is typically injected at the medium voltage (“MV”) substation, bypasses low voltage (“LV”) transformers and is delivered to the end-users' electricity sockets in their home or business.
The diagram below (Inductive Coupling Injection Technique) shows how the BPL injector converts the IP data traffic into an RF signal in a signal cable. The signal is then injected into the MV or LV cable by induction using ferrite cores. This is known as “inductive coupling” and can be done without switching off power. An alternative injection technique, known as “conductive coupling” connects the signal cable directly to the electricity cables but requires the power to be switched off during connection for safety reasons.
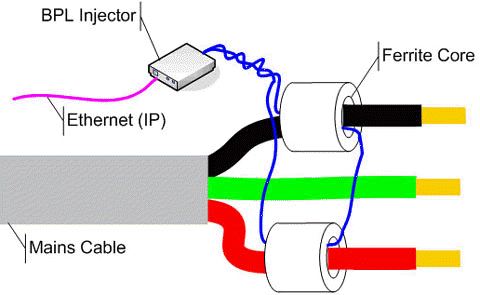
Inductive Coupling Injection Technique
The end-user simply connects a BPL modem to any power socket in the building for access to the BPL RF signal. The BPL modem converts the RF signal back into IP data. The end-user then connects the BPL modem into a computer, server, switch, or wireless access point.
There are two basic types of BPL solutions, “access” and “in-building”. Typically, access BPL connects the MV substation to the consumer's premises, whereas in-building BPL is a Local Area Network replacement technology used to connect offices or units within a multiple tenant building. Different technologies are generally used for these different solutions.
Note that in some countries, the technology discussed in this document is referred to as PLC or Power Line Communications. This term should not be confused with the term Power Line Carrier also referred to as PLC. Power Line Carrier is a narrowband communications technology typically operating at 75bps using the 9.6kHz frequency band often used with Automatic Meter Reading and SCADA systems.
There are a number of basic applications for this BPL technology:
1. BPL can provide communications connectivity for Distribution Automation applications such as remote capacitor control, automatic meter reading and remote ON/OFF capabilities, among others. These applications are covered in more detail in the next section
2. BPL can be used to create an IP access network to solve the "Last-Mile" dilemma. Since the Grid is available throughout the country, BPL is simply an add-on to that existing electrical infrastructure which will allow every consumer to gain access to the Internet. Customer applications such as WWW access, Voice over Internet Protocol, video on demand, telemedicine, and distance learning can be established on these systems.
3. Since the BPL network touches all of the electrical components connected to the electrical grid, there is an opportunity to install monitoring and security devices anywhere on the Grid which has been BPL enabled. The BPL network provides 2-way high-speed communications to all of these devices. Devices could include:
— Security Cameras
— Biological Contaminant detection
— Gas / Chemical detection
— Corrosion monitoring
— Pipeline Monitoring
ElectroNet expect to be able to provide a Broadband service based on BPL for an entry price similar to existing dialup services, but with the ability to go up to 2Mbps to the consumer at a higher fee.
An important principle of BPL technology is that it does not affect the normal operation of the Grid, or the transmission and distribution of electricity to the consumer. BPL equipment is designed with this in mind, and both theory and practical tests have shown that BPL does not affect normal operation of the Grid.
1. The frequencies used by BPL technology (typically 1MHz to 35Mhz) are outside the range that would affect the Grid, and the power used (typically 0.1Watt) is insignificant compared to the power transmitted by the Utility to the consumer.
2. Detailed tests demonstrating that BPL does not affect the normal operation of the Grid, or the transmission and distribution of electricity to the consumer have been carried out by approvals bodies in a number of countries. Electonet's consultants have participated in and observed some of these tests, for example in Malaysia
3. ElectroNet will conduct a Pilot Project that will have as key success criteria a determination that BPL does not affect the normal operation of the Grid, or the transmission and distribution of electricity to the consumer.
A large number of utilities throughout the world are currently conducting trials or commercial operations of BPL. Some have already begun commercial operations:
1. In Germany, the service is commercially offered :
— in Mannheim under the name "Vype" www.vype.de
— in Hameln under the name "Piper-Net" www.piper-net.de
— in Dresden under the name "PowerKom" www.drewag.de
— in Offenbach under the name "EVOpowerline" www.evo-ag.de
2. In Austria, the service is commercially offered in the city of Linz under the brandname "Speed-Web" www.linzag.net.
3. In Poland, the service is offered in the city of Krakow.
4. In Scotland, the service is offered in the cities of Crieff and Campbeltown under the name of "Broadband" www.hydro.co.uk/broadband.
5. In Malaysia, Realm Energy is beginning pre-commercial deployment from March 2005, having conducted a successful trial in the University Tenaga Nasional.
6. In Spain Endesa and Iberdrola are in commercial deployment.
7. In the US, the service is offered by:
— Pennsylvania Power & Light
— Cinergy
— Progress Energy
— City of Manassas (municipal owned utility)
— Central Virginia Co-op
Other commercial deployments are already in operation in China, Hong Kong, Singapore and Korea.
The SMART GRID is a utility operations solution that has advanced capability and provides automation of electrical grids. It has three components:
· Intelligent physical devices that are either part of the grid (such as capacitors or automatic meter readers), or connected to the grid (such as remote cameras)
· A 2-way BPL communications network that connects the physical devices to the control centre where the data is stored.
· A set of applications and algorithms that process the collected data to provide high level, high value information and can control the physical devices.
The diagram below (AMR Architecture) shows how consumer meter readings are collected by the Data Collector and then transmitted back to the Operations Centre via BPL and fiber backhaul. Relays or remote ON/OFF devices connected to the network can also be actively controlled.
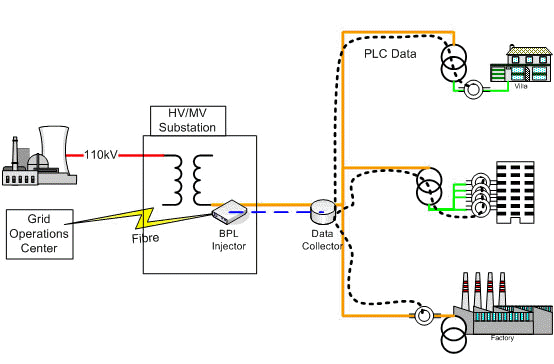
AMR Architecture
BPL (described in the previous section) is an enabler for the SMART GRID, providing the communications from the data collector to the control centre, allowing data collection as well as remote control of the intelligent devices.
|
AMR |
Automatic Meter Readers. Intelligent Meter Readers which can transmit meter readings and other data back to the Utility Operations Center using Power Line Carrier |
|
BPL |
Broadband over Powerline. A high speed (512Kbps and above) IP network using the Grid for transmission. |
|
PLC / Power Line Carrier |
Power Line Carrier is a narrowband communications technology typically operating at 75bps using the 9.6kHz frequency band often used with Automatic Meter Reading systems. |
|
SMART GRID |
The SMART GRID connects intelligent physical devices on the Grid using a 2-way BPL communications network to the control centre where a set of applications and algorithms process the collected. |
|
Distribution Automation |
Distribution Automation is the use of various utility applications to improve the efficient management of the Grid. |
|
Grid |
The Grid is the Utility's electrical grid infrastructure. |
|
Mbps / Kbps / bps |
Megabits per second / Killobits per second / bits per second. |
|
MHz / KHz |
Megahertz / Kilohertz |
|
GSM/GPRS |
GSM is the technology used for cellular operation in Saudi Arabia. GPRS allows direct data transmission over GSM. |
|
Data Collector |
A device that collects information from AMRs and allows control of intelligent devices on the Grid. Connects back to the Utility control center through the BPL network. |
|
|
|
Send E-mail to
TSN@The-Saudi.Net with questions or
comments about The Saudi Network. We are Looking for Business Sponsorship or Marketing Partnership |